- 4 -
c. -9000 to -8347
Early Boreal Mesolithic
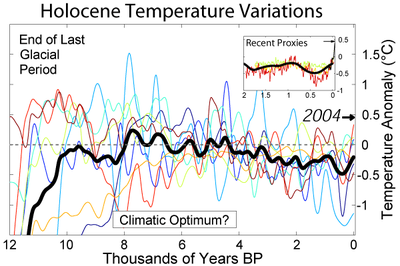
1. The Early Hypsithermal
2 As above, So below: Neolithic Cultural Mimesis
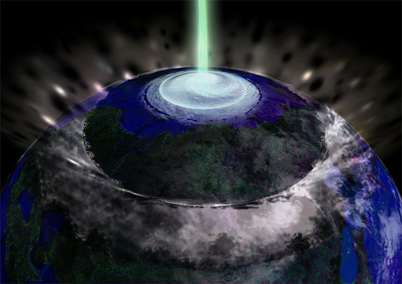
3. From Day to Night (c. -8347)i. Peratt Column collapses, ball plasmoids depart
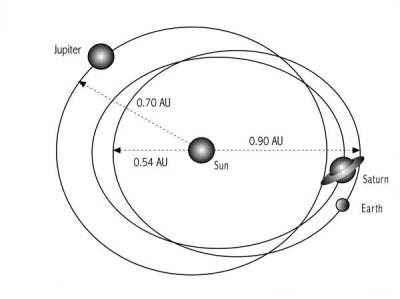
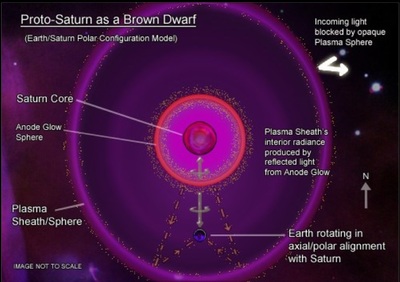
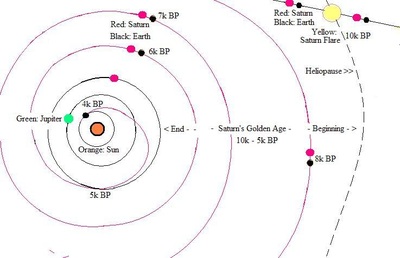
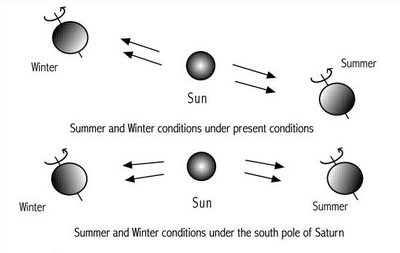
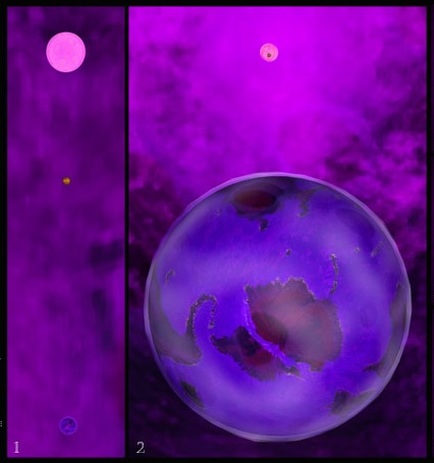
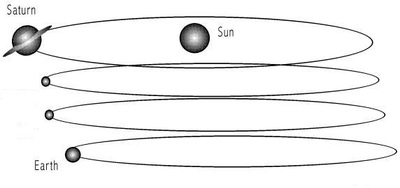
a. Genesis 1:4-5 -- “Day One” b. Maori mythos c. Quiche Maya mythos d. Mesoamerican cosmology - Popul Vuh e. Crow cosmology f. Hopi cosmology g. Phoenix’s triple death-rebirth h. Vishnu measures the Earth (three times) i. Long Count 1.0.0.0.0 as end of “First Creation” j. 10.3 Kiloyear Event ii. Polar Configuration now visible; plasmasphere shrinking a. Mesoamerican - Council of 6 Gods b. Powers Overhead in the North (Cook, &c.) iii. Glowing stream of archaic Axis Mundi (Talbott Column) a. Talbott (1980 &c.) b. Cook (2001 &c.) c. van der Sluijs (2007 &c.) |
i. Early communal settlements
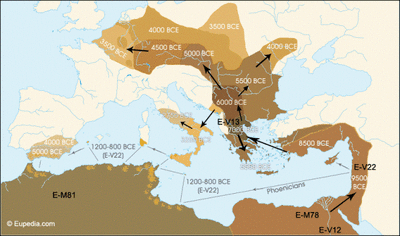
a. Göbekli Tepe (continued) (-9130 to -8800) b. Nevalı Çori c. Çayönü d. Early Levantine tells (-9000 to -8500) e. Lepenski Vir, Danube (early settlements) (-9500 to -7200) f. Doggerland fishing bank (-9500 to -6200) ii. Creative novelties of Neolithic culture a. Formative aspects of culture - Language - Social organization - Proto-religious sentiments b. Artifacts demonstrate lack of violence & warfare |