- 1 -
c. -10,900
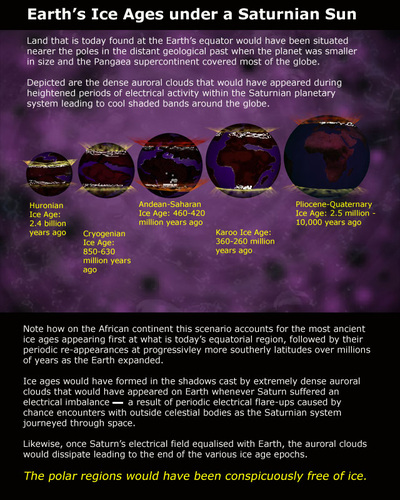
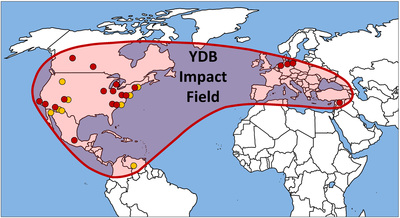
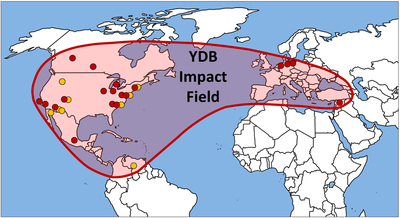
Late Glacial Maximum Extinction Event
1. Interplanetary electrical discharge machining
|
|
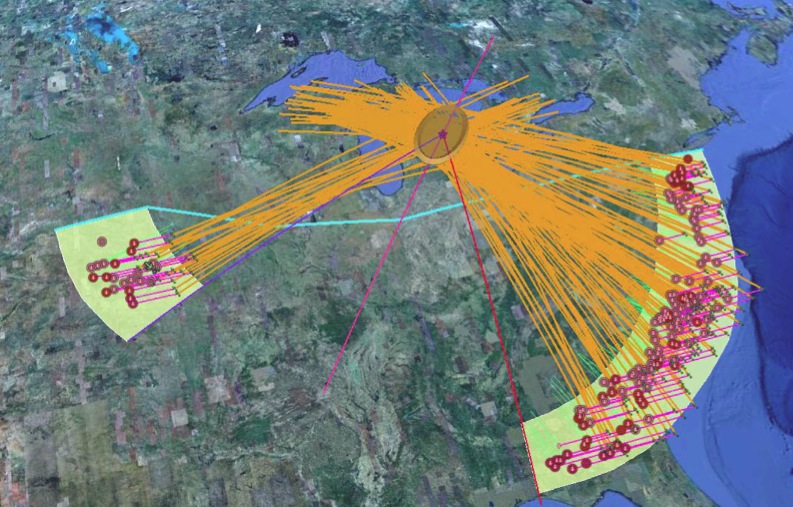
i. Birkeland field current
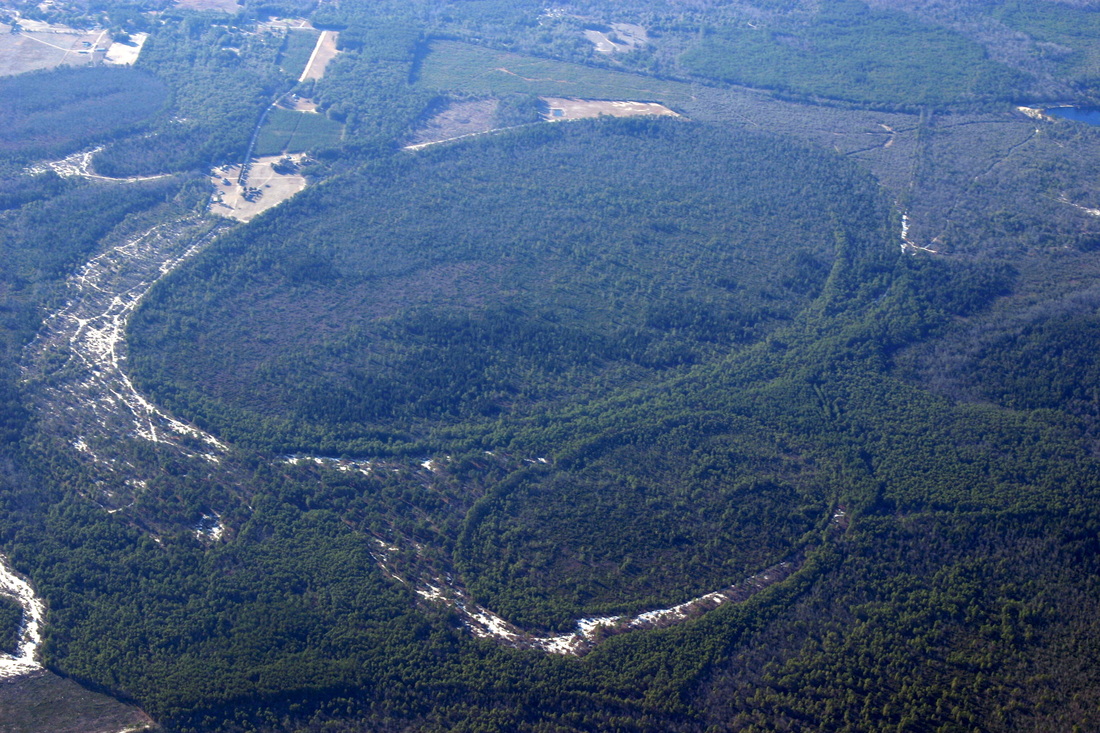
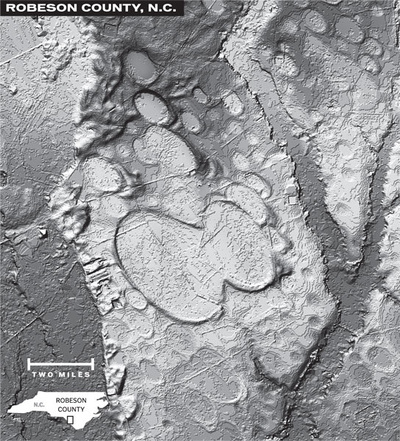
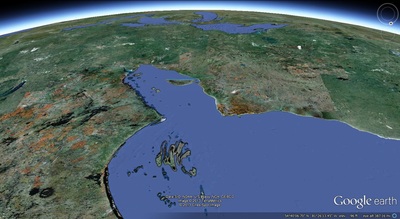
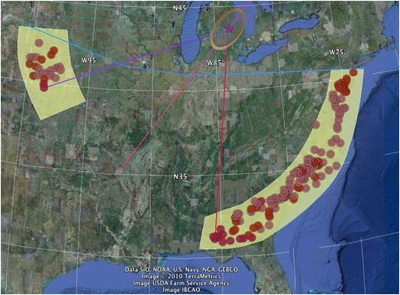
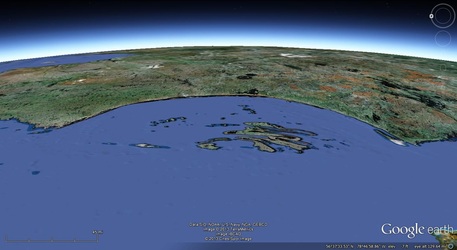
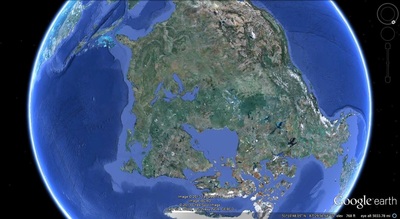
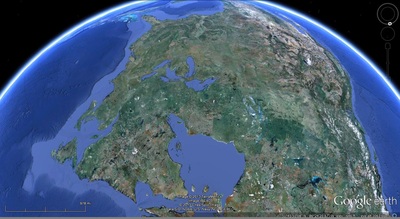
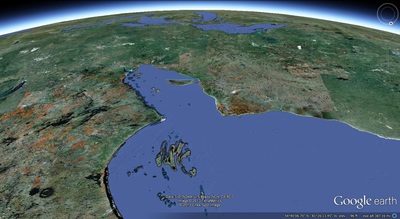
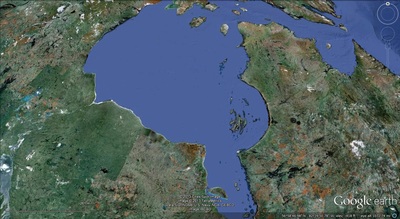
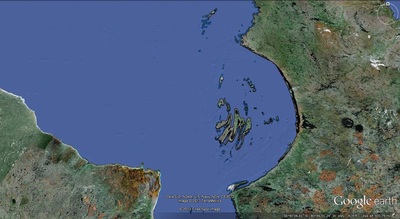
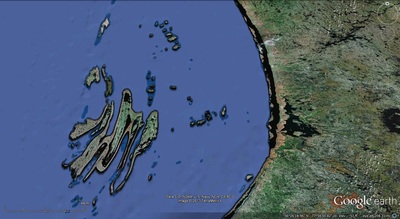
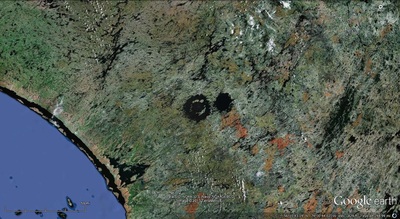
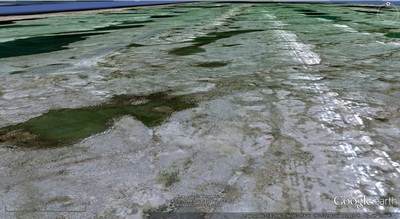
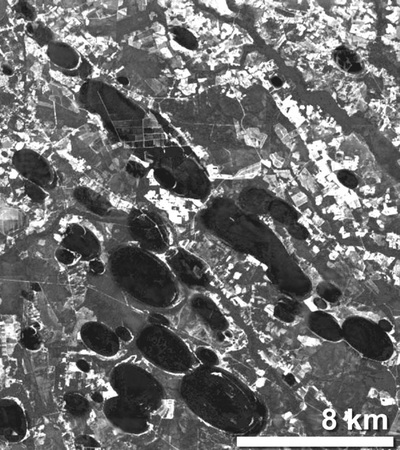
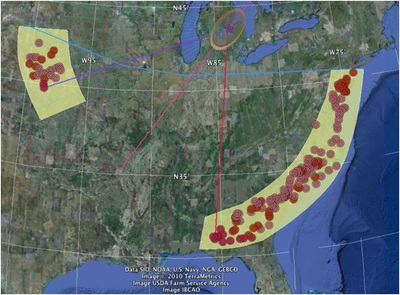
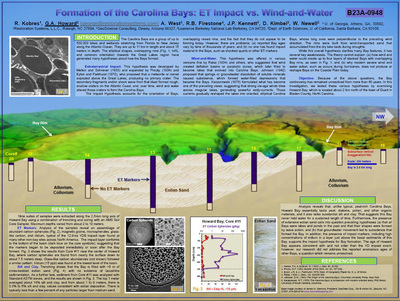
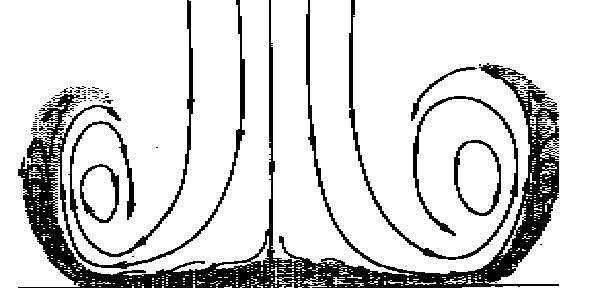
a. Proto-Saturn nebula attracted to Sun b. Proto-Saturn’s large positive charge, repulsive shock c. 280-mile wide anode blister, Hudson Bay d. Tortured landforms of Sanikiluaq(Belcher Islands) ii. Charge equilibration a. Proto-Saturn dumps electrons to equilibrate, scarred satellites b. gouges on continental shelf, boring points, blistering c. rapid flowing meltwater, formation of eskers & drumlins iii. Earth torque, heliarc sculpting a. Saginaw Impact Manifold, carving of Great Lakes b. Rapid flowing meltwater, formation of glacial terrain iv. Vortical ejecta a. Carolina-Nebraska sandhills & bays b. Carbon spherules |
2. Repulsive shock
|
i. Compressive shock wave generates high temperatures
a. Incinerates forests and prairies (N. America) b. Boils lakes and rivers (N. America) c. Incinerates all plant and animal life; tar pits d. Repulsive folding of Appalachian & Rocky mountains e. Clovis Point culture terminated ii. Archaic Inferno Forces in mythology a. Purusha, Brihadaranyaka Upanisad (Hindu) b. Gor the Father, Chilam Balam (Mesoamerican) |
3. Antipodal shockii. Antipodal Earth-shock and crust displacement
ii. South Indian Ocean |
4. Alteration of Earth's axis & orbital period
|
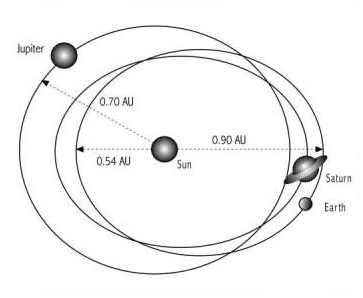
i. Yukteswar (1894)
a. Sun relocates away from Grand Center (Proto-Saturn) ii. Cardona (1982 &c.) iii. Thornhill (1998 &c.) i. Proto-Saturn attracted to Sun iv. Cook (2001 &c.) a. Saturn’s orbital period reduced b. Earth’s synchronous rotation ends; subpolar rotation begins |